We've all been patients at some point, but our journeys were not the same. Patient journey mapping holds the key to unraveling this mystery, providing a strategic lens into the diverse pathways individuals tread throughout their healthcare experiences.
In this article, we'll explore the pivotal role of patient journey mapping in the healthcare industry, uncovering its profound benefits for both providers and patients. From amplifying patient satisfaction to streamlining operational processes, the impact is transformative.
But how does one embark on this journey of understanding and improvement? We'll guide you through the essential steps and considerations, offering insights into the art of crafting a meaningful healthcare patient journey map.
Join us as we peel back the layers of patient experience journey mapping. This powerful tool not only illuminates the complexities of healthcare but also empowers providers to reshape and enhance the patient experience.
Contents
What is a patient journey?

A patient journey is the entire process a person goes through when seeking and receiving a healthcare service. It covers everything from first noticing symptoms or realizing the need for care and medical attention to finally resolving the health issue. The journey involves patient interactions with healthcare professionals, diagnostic procedures, treatment activities, and follow-up care.
Mapping and understanding the patient journey can help boost the quality of hospital care and improve patient satisfaction. By pinpointing challenges, patient communication gaps, and areas for enhancement, care providers can refine their services to better cater to patients' needs. It also contributes to promoting patient-centered care, shifting the focus beyond just treating diseases to considering the overall well-being and experience of the patient.
Difference from other customer journeys
While the concept of patient journey mapping is similar to customer journey mapping, there are unique aspects specific to the healthcare domain. This is how a patient journey differs from any other customer journey:
- Emotional intensity. Health-related experiences often involve heightened emotions, including fear, anxiety, uncertainty, a sense of losing control, and a dependence on others. The emotional aspect is more pronounced in patient journeys compared to customer journeys in most industries.
- Complexity and uncertainty. Healthcare journeys often involve multiple stakeholders, various diagnostic and treatment options, and inherent uncertainties. Navigating these complexities requires a different approach compared to more straightforward consumer experiences. Comparing buying eyeglasses online and visiting a doctor — both are experiences, but how different they are!
- Regulatory and ethical considerations. Healthcare is heavily regulated, and ethical considerations play a significant role there. Patient journeys must align with regulatory standards and ethical principles that other industries don’t have.

- Clinical decision points. Patient journeys involve critical clinical decision points, such as diagnosis and treatment choices. These decisions not only impact the patient's health but also influence the overall trajectory of the journey.
- Care continuum. Patient journeys often extend beyond a single episode of care. They may involve long-term management, follow-up appointments, and ongoing support, creating a continuous care continuum.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration. Healthcare is often delivered by a team of professionals from different disciplines. The patient journey may involve collaboration among physicians, nurses, specialists, and other healthcare providers.
Patient journey mapping benefits

Mapping a patient journey offers a range of benefits that contribute to improving the overall quality of healthcare delivery. Here are some key advantages:
- Visualization of the entire patient journey helps healthcare providers identify critical patient journey touchpoints that impact patient satisfaction and experience and require immediate attention. By paying more attention to these touchpoints, you ensure a more positive overall journey.
- Gaps in care and challenges are highlighted among healthcare professionals. Addressing these issues ensures a more seamless and collaborative approach to patient care.
- Pain points and barriers become evident, enabling healthcare providers to proactively address issues that may hinder effective care delivery.
- Understanding individual patient journeys allows for more personalized ongoing care plans. Tailoring interventions to specific needs and preferences improves patient engagement and outcomes.
- By mapping a patient journey, you can identify resource-intensive stages and areas where efficiency can be improved, enabling a healthcare organization to allocate resources more effectively.
- It's a great way to identify opportunities for smoother transitions between different stages of care, ensuring continuity and preventing gaps in treatment.
- It becomes clear where patient involvement in the decision-making process can contribute to their healthcare journey.
Example: Tom, recovering from surgery, feels more empowered as his healthcare team provides clear post-operative care instructions, making him an active participant in his recovery.
In summary, patient journey mapping provides a comprehensive framework for healthcare improvement, addressing specific challenges at each stage and leading to tangible enhancements in patient experience, communication, and overall care delivery.
Patient journey stages
Patient journeys can differ, and if we take a broad perspective, some key stages would include:
Awareness
This stage involves the patient recognizing symptoms and becoming aware of a potential health issue.
- Key considerations: Pay attention to how patients identify and interpret their symptoms, as well as the information sources they consult.
Example: John notices persistent joint pain and, through online research, suspects it might be arthritis. His journey begins with a heightened awareness of his symptoms.
Seeking information
Patients actively look for information to understand their symptoms, potential causes, and the importance of consulting a healthcare professional.
- Key considerations: Review the information sources patients use and how well they understand the need for professional medical advice.
- Example: Emily researches her persistent cough online, learning about various respiratory conditions and recognizing the importance of seeing a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
First contact
This marks the initial interaction with the healthcare system, typically through scheduling an appointment with a primary care physician.
- Key considerations: Assess the ease of access to healthcare services and the patient's initial experience with medical professionals.
- Example: Alex schedules an appointment with his family doctor to discuss recent changes in his vision, initiating his journey within the healthcare system.
Diagnostic process
Patients undergo diagnostic tests to identify the root cause of their symptoms.
- Key considerations: Examine the efficiency of the diagnostic process and the clarity of communication about the tests.
- Example: Maria undergoes blood tests and imaging to determine the cause of her abdominal pain, marking the diagnostic phase of her journey.
Treatment planning
Patients receive a diagnosis, and healthcare providers collaborate on creating a personalized treatment plan.
- Key considerations: Evaluate how well the diagnosis is communicated and involve patients in treatment decisions.
- Example: Emily receives a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Her healthcare team takes the time to explain the condition, discusses various treatment options, and actively involves her in deciding on a comprehensive plan that combines medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Treatment and clinical care service
Patients initiate the recommended treatment plan, experiencing the day-to-day challenges and improvements associated with their patient journey in a hospital.
- Key considerations: Monitor treatment adherence, side effects, and the patient's overall experience during this active phase.
- Example: Sarah starts chemotherapy for her cancer, navigating the treatment process with the support of her healthcare team.
Psychological support
Patients deal with the emotional toll of managing a health condition, including anxiety, frustration, or isolation.
- Key considerations: Acknowledge and address the emotional aspects of the journey, providing resources for mental health support.
- Example: James copes with the emotional challenges of managing chronic pain, seeking counseling to navigate the psychological impact.
Regular checkups
Patients undergo routine checkups to monitor their health status and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Key considerations: Ensure consistent communication and scheduling of regular checkups to track progress and address any emerging issues.
- Example: Sarah, diagnosed with hypertension, attends regular checkups where the healthcare team monitors blood pressure, discusses lifestyle adjustments, and ensures medication efficacy. The routine checkups create a proactive approach to managing her condition.
Feedback
Patients provide feedback on their experiences, allowing healthcare providers to refine and tailor their care.
- Key considerations: Establish mechanisms for patients to share feedback easily and transparently, encouraging an open dialogue.
- Example: John shares his experiences with a new treatment plan, providing feedback on its effectiveness, side effects, and overall impact on his daily life. This feedback loop allows the healthcare team to make timely adjustments and improve the patient's journey.
The stages may vary based on diverse scenarios and individual health circumstances. For instance, when a patient undergoes surgery or faces an acute medical event, the trajectory of their journey can diverge significantly from a more routine healthcare experience.
Factors such as the need for emergency care, hospitalization, and specialized interventions can introduce unique stages and considerations. Additionally, variations may arise due to the specific nature of medical conditions, treatments, and the individual preferences and needs of patients.
Recognizing this variability is crucial for comprehensive journey mapping, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the patient experience across different healthcare contexts.
Types of healthcare journey maps

Healthcare journey maps can take various forms depending on their focus, purpose, and the specific aspects of the patient experience they aim to understand.
Here are a few types of healthcare journey maps:
Clinical journey maps
Focus: Emphasize the clinical aspects of a patient's experience, including diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
Purpose: Help healthcare providers understand the medical processes and interventions involved in the patient's journey.
Example: A clinical journey map for a cancer patient would detail the steps from initial symptoms to diagnosis, treatment modalities, and post-treatment care.
Service delivery maps
Focus: Highlight the various touchpoints and services a patient encounters throughout their healthcare journey. Then, detail the back and front processes your team does or has to do during each stage.
Purpose: Enable healthcare organizations to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of service delivery.
Example: Mapping the service delivery for a patient undergoing surgery, including preoperative consultations, surgical procedures, and post-operative care.
Digital journey maps
Focus: Examine the patient's interaction with digital tools and technologies, such as online portals, mobile apps, and telehealth platforms.
Purpose: Help improve the digital aspects of patient engagement and communication.
Example: Mapping the patient's journey when using a telehealth platform for virtual consultations, prescription refills, and accessing medical records.

Chronic disease management maps
Focus: Explore the long-term journey of patients managing chronic conditions.
Purpose: Aid in understanding the challenges and opportunities for supporting patients in their ongoing self-management.
Example: A journey map for a diabetes patient would encompass regular monitoring, medication management, lifestyle adjustments, and periodic checkups.
Emergency care journey maps
Focus: Examine the patient’s experience during emergencies, from the onset of symptoms to emergency room admission and follow-up care.
Purpose: Help optimize response times, communication, and the overall emergency care process.
Example: Mapping the journey of a patient experiencing chest pain, from the initial call to emergency services to the triage process and subsequent cardiac care.
Pediatric patient journey maps
Focus: Tailored specifically for the unique needs and considerations of pediatric patients and their families.
Purpose: Address the emotional and practical aspects of pediatric healthcare experiences.
Example: Such a map is good for a child undergoing surgery to consider the role of parents, age-appropriate communication, and post-operative care.
Palliative care maps
Focus: Center on the patient's journey when facing serious illness, with a focus on providing comfort and support.
Purpose: Enhance the quality of life for patients and their families during end-of-life care.
Example: This kind of journey map suits a patient receiving palliative care when considering symptom management, emotional support, and coordination of services.
The mentioned types of maps cover different patient scenarios and clinical cases. There can also be "AS-IS" and "TO-BE" maps, reflecting the current state of the journey and the desired one, respectively.
All these types of healthcare journey maps offer a nuanced understanding of the diverse aspects of patient experiences, allowing healthcare providers and organizations to tailor their services to meet the unique needs of different patient populations.
How to do patient journey mapping?

Mapping a patient's journey is a thorough process that needs careful planning, teamwork, and analysis. Here's a guide on how to do it:
- Define the objectives
Clearly articulate the goals of the patient journey mapping exercise. Determine what aspects of the patient experience you want to understand and improve. All involved parties should be aware of these goals and agree with them.
- Assemble a cross-functional team
Form a team that includes representatives from various departments, including healthcare providers, administrative staff, patient advocates, and anyone involved in the patient experience.
- Do research
Conduct thorough research to gather quantitative and qualitative data related to the patient experience. This may involve analyzing patient records, studying existing feedback, diving into analytics and market research, and reviewing relevant literature on best practices in healthcare.
- Select a patient segment
Identify a specific patient segment or persona to focus on. This could be based on demographics, health conditions, or specific healthcare services.
Tip: You can leverage your segments or patient personas to craft an empathy map, which is particularly valuable in healthcare.
- Conduct stakeholder interviews
Interview stakeholders, including healthcare professionals and administrative staff. Gather insights into their perspectives on the patient journey, pain points, and opportunities for improvement.
- Define the stages
Outline the patient journey by mapping out each stage and interaction with the healthcare system. This can include pre-visit, during a visit, and post-visit experiences.
Tip: To speed up the process, run a journey mapping workshop with your team. It will help with the next step, too.
- Create the patient journey map
Develop a visual representation of the patient journey. This can be a timeline or infographic that illustrates each stage, touchpoint, and the emotional experience of the patient.
- Identify pain points and opportunities
Analyze the collected data to pinpoint pain points, areas of friction, and opportunities for improvement. Consider emotional, logistical, and clinical aspects of the patient experience.

- Review and validate
Consider collaborative journey mapping. Share the draft patient journey map with stakeholders, including frontline staff and patients, to validate its accuracy. Incorporate feedback to ensure a comprehensive and realistic representation.
- Develop actionable plans
Generate specific, actionable plans based on the identified pain points and opportunities. Each initiative should be feasible, considering resources and organizational constraints.
- Prioritize and implement changes
Prioritize the recommendations based on impact and feasibility. Begin implementing changes that address the identified issues, whether they involve process improvements, staff training, or technology enhancements.
- Monitor and iterate
Continuously monitor the impact of implemented changes. Gather feedback from both staff and patients to understand the effectiveness of the improvements. Iterate on the patient journey map and make recommendations as needed.
- Measure your success
You can also establish KPIs to measure the success of any improvements made based on the patient journey mapping insights. These could include patient satisfaction scores, reduced wait times, or improved communication metrics.
- Document insights (optional)
And keep a record of the lessons learned during the patient journey mapping process. This documentation can inform future initiatives and contribute to ongoing efforts to enhance the patient experience.
- Promote a culture of continuous improvement
Foster a culture within the organization that values continuous improvement in patient care. Encourage ongoing feedback and regularly revisit your journey map to ensure its relevance over time.
By following these steps, healthcare organizations can gain valuable insights into the patient experience, leading to targeted improvements that enhance healthcare quality and patient satisfaction.
How to improve the patient journey?

Striving for a seamless patient journey involves enhancing the overall experience that individuals have when seeking and receiving healthcare services. Here are some strategies to consider:
Patient-centered care
- Prioritize patient needs and preferences.
- Emphasize education and empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey.
- Foster open communication and active listening.
Streamlined access to care
- Reduce wait times for appointments and procedures.
- Implement online scheduling and appointment reminders.
- Provide options for virtual consultations when appropriate.
Effective communication
- Ensure clear and understandable communication with patients.
- Provide information about treatment plans, medications, and follow-up care.
- Confirm that patients are well-informed about the potential risks and benefits of treatment options.
Education and empowerment
- Offer educational resources to help patients understand their conditions and treatment options.
- Encourage patients to actively participate in their health management.
- Provide tools for self-monitoring and self-management when possible.
Care coordination
- Improve collaboration and communication among healthcare providers to strengthen care coordination, ensuring a more cohesive and seamless experience for patients throughout their healthcare journey.
- Define and implement standardized protocols for communication and handovers between care teams, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring continuity of care.
- Implement remote monitoring technologies to track patients' health remotely, enabling timely interventions and reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
Technology integration
- Adopt electronic health records (EHRs) for efficient information sharing.
- Use telemedicine to enhance accessibility and convenience.
- Implement mobile health apps for appointment reminders, medication management, and health tracking.
Feedback and continuous improvement
- Conduct regular surveys to gather specific insights into patient satisfaction, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of their experiences.
- Establish easily accessible channels for patients to provide real-time feedback, ensuring that their voices are heard promptly.
- Respond promptly to patient feedback, address concerns, and communicate any changes or resolutions, fostering a sense of responsiveness and accountability.
Cultural competency
- Train healthcare staff to be culturally competent and sensitive to diverse patient needs.
- Promote diversity in healthcare staff to reflect the communities served, fostering a more inclusive and culturally sensitive environment.
- Recognize and celebrate cultural awareness events within the healthcare setting, fostering an inclusive atmosphere that appreciates the richness of diverse traditions.
Emotional support
- Address the emotional and psychological aspects of healthcare.
- Provide resources for mental health and emotional well-being.
- Consider support groups or counseling services.
Efficient billing and financial assistance
- Simplify billing processes and provide clear information about costs.
- Offer financial assistance programs for patients in need.
- Communicate transparently about insurance coverage and out-of-pocket expenses.
Staff training:
- Train healthcare staff in patient-centered communication and empathy.
- Ensure staff is knowledgeable about the resources available to patients.
- Foster a culture of empathy and compassion in the healthcare environment.
By focusing on these aspects, healthcare providers can contribute to a more positive and effective patient journey. Regularly reassessing and adapting strategies based on feedback and evolving healthcare trends is crucial for ongoing improvement.
Templates
UXPressia already has some healthcare journey map examples:
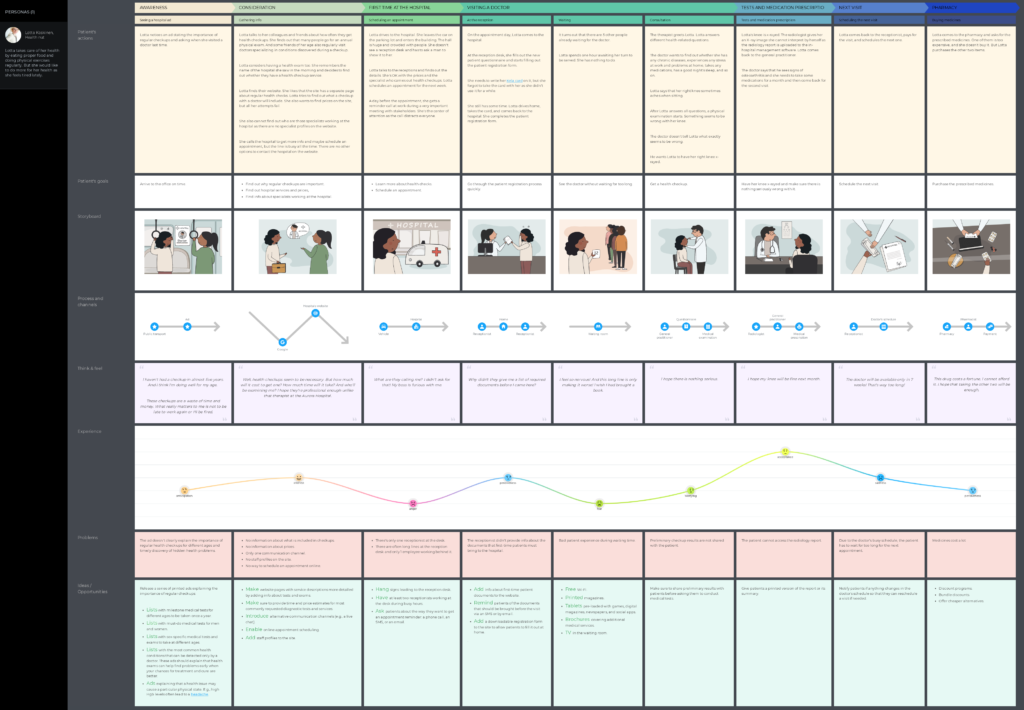
- Surgical patient journey
This map focuses on the healthcare journey of a patient persona, Robin, from the moment when the patient understands that something is wrong to the recovery period. This journey is long and very detailed.
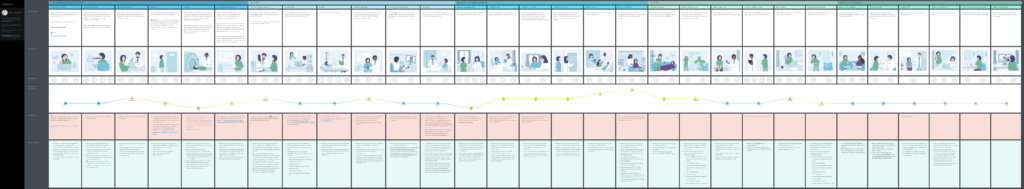
- Non-surgical patient journey
This map visualizes the journey of a patient, Lotta, who decides to undergo a checkup at a hospital. She schedules a visit, gets a consultation, takes some tests, and starts taking some medicine prescribed by her doctor.
More healthcare and well-being templates are available in our library.
Wrapping up
In wrapping up, think of patient journey mapping as a powerful tool reshaping the healthcare landscape, with the patient's experience taking center stage. It's like creating a roadmap that intricately traces every step of a patient's interaction within the healthcare system.
This deliberate mapping isn't just a plan; it's a compass guiding healthcare organizations toward key points where they can enhance patient satisfaction, simplify access to care, and cultivate a more compassionate and patient-focused healthcare environment. Investing in patient journey mapping is more than a strategy—it's a dedication to raising the bar in care quality, amplifying the patient's voice, and ensuring that every leg of the healthcare journey is characterized by empathy, understanding, and an unwavering pursuit of excellence in patient experience.