Now that you know what a persona is, how to create it, and why your company really needs to use personas, it's time to answer one more question. What is a buyer persona, and what is a user persona? Is there any difference between these two? To put it short, there is. But should you care? Most likely, you should. In this post, we'll highlight the key differences between buyer and user personas.
Contents
- 1 The main difference
- 2 How to create a user persona?
- 2.1 Step 1: Define your purpose and goals
- 2.2 Step 2: Conduct research
- 2.3 Step 3: Identify demographic information (if you need it)
- 2.4 Step 4: Explore your user persona goals and objectives
- 2.5 Step 5: Determine their pain points and challenges
- 2.6 Step 7: Create a user persona profile
- 2.7 Step 8: Validate and refine
- 2.8 Step 9: Use personas in decision-making
- 3 How to create a buyer persona?
- 3.1 Step 1: Define your purpose and goals
- 3.2 Step 2: Conduct market research
- 3.3 Step 3: Identify your buyer persona demographic information
- 3.4 Step 4: Explore goals and challenges
- 3.5 Step 5: Determine buying behavior
- 3.6 Step 6: Find out information sources
- 3.7 Step 7: Create a buyer persona profile
- 3.8 Step 8: Validate and refine
- 3.9 Step 9: Use buyer personas
- 4 Summary
The main difference
The key difference is that a buyer persona isn't necessarily a user. But they can be.
And that's all there is to it. A good example would be a laptop. You may buy one for your own use, and, in this case, you'll be both a buyer (as you purchased it) and a user persona (as you are using the computer) at the same time. But what if you buy a laptop for your mom? Or for an employee? You're still the buyer. But not the user.
This difference between user and buyer personas might seem obvious, and it really is. However, what does this difference mean for us as UX designers, product managers, marketing professionals, or sellers?
It simply means we should keep both buyers and users in mind when designing products or services, mapping customer journeys, and creating marketing campaigns. Why? Because buyer and user personas often have different goals and expectations. Now, let's look at each persona type and its characteristics.
User persona

As noted earlier, a user persona isn't necessarily someone who buys from you. They are those who use your product or service. It might not even be their decision (for example, Jake, a graphic designer, worked in Adobe for a long time, but he had to switch to CorelDRAW at his new job as his new company mandates the use of this software for all graphic design tasks). User personas may even dislike your product but still have to use it because of their external factors (e.g., because of their management).
While decision-makers' higher-level goals focus on costs and long-run benefits, end-users' goals are more straightforward but no less important. They may expect something like ease of use, simple navigation, and clarity of what to do at each stage. Anything that makes their routine operations less routine and their day a little brighter.
While creating user personas, pay attention to their skills and, for example, what technology they use as well as their previous experience, as this might shift your perspective on your product or service.
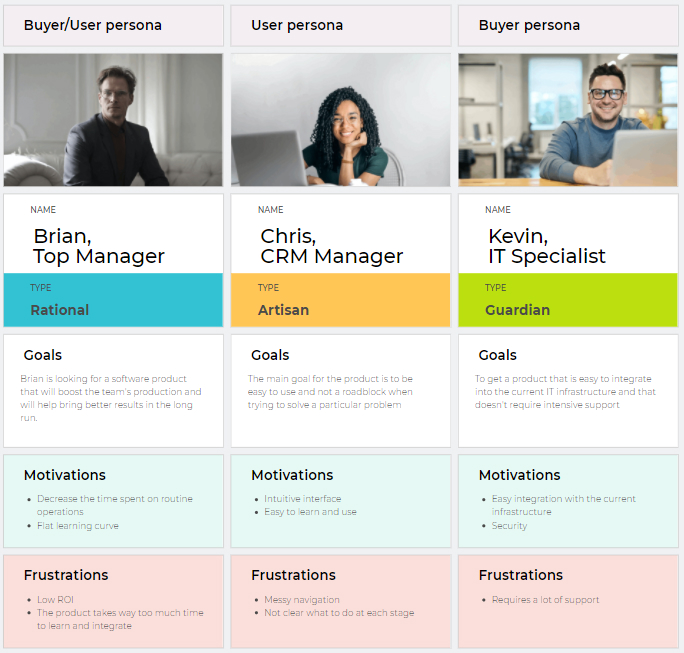
Buyer persona
A buyer persona is slightly more complex than an end user. Often, it's a team of decision-makers who decide whether to purchase something or not. It could be supervisors, managers, IT guys, and so on. And each of them has their own ideas of what should be in your product.
For example, a manager or supervisor might want to know whether your product will boost their team's productivity. And, if yes, by how much? How easy will it be to adopt your solution and teach employees?
The finance department will want to see the economic benefits, while the executive team will focus on how your solution will support their higher-level goals.
An IT specialist will definitely ask about the costs of supporting your system. How reliable and secure is it?
It isn't easy to keep track of all of them, but it is necessary. It might even turn out that you'll have to create multiple personas for each decision-maker.
Now that you know how to differentiate between these two types of personas, let’s dig a little deeper and talk about how to create them.
How to create a user persona?

Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a user persona, along with examples:
Step 1: Define your purpose and goals
Before doing anything, it’s important to determine why you need user personas, and it will be your project goal, which will guide your persona creation process. Are you designing a product, developing content for landing pages, or planning a marketing strategy?
- For product and design teams, effective user personas provide a nuanced understanding of users' goals and pain points. Persona-driven insights allow design teams to create products that not only meet functional requirements but also align with the emotional and practical needs of the intended audience.
- From feature prioritization to user interface design, personas guide decisions, ensuring that the final product is tailored to the specific expectations of the target users.
- For the content team, understanding user personas' preferences and interests enables content creators to develop material that speaks to the audience. This targeted approach results in content that is not only more relevant but also more likely to capture and retain the audience's attention, developing a connection with them.
- In the marketing department, personas serve as the foundation for developing strategies that target specific audience segments. Such persona-based targeted campaigns can be more effective in reaching potential customers, increasing conversion rates, and maximizing the return on investment. Understanding the motivations and challenges of user personas allows marketers to personalize their messaging. This personalization creates a stronger connection with the audience, fostering brand loyalty and trust.
- For the UX department, personas can help inform design decisions by highlighting user behaviors and preferences. This leads to a more user-centric approach, resulting in products that function well and provide an enjoyable and intuitive user experience. As user personas evolve, the iterative process of product development can be informed by ongoing user feedback and changing preferences, ensuring a dynamic and responsive user experience.
So, determine your goal, and let’s proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Conduct research

Gather information about your target audience through various sources:
- Running surveys is a powerful way to collect a range of data, from basic demographics to nuanced preferences and behaviors.
- Utilizing analytics tools is akin to peering into the digital footprints of your audience. This method unveils patterns, trends, and user behaviors that inform strategic decisions.
- Engaging in direct conversations with real users is akin to stepping into their shoes, gaining qualitative insights that breathe life into persona profiles.
- Analyzing social media interactions provides a real-time window into user sentiments, preferences, and discussions.
Beyond the named methods, be open to exploring various other sources that may yield unexpected yet invaluable insights.
Step 3: Identify demographic information (if you need it)
Define the basic characteristics of your users in case this data somehow impacts the way people use your product or service, their buying decisions, or you are planning, for instance, to launch online ads where including this information is crucial. You will have something like this:
- Age: 25 years old
- Gender: Non-binary
- Occupation: Product Manager
- Education: Bachelor's degree in Computer Science
Step 4: Explore your user persona goals and objectives
Embark on a journey to unravel the aspirations and objectives driving your user's engagement. Understanding their goals paints a vivid picture of the outcomes they seek and allows you to tailor your offerings to align seamlessly with their ambitions.
- Primary goal
Delve into the central objective that propels your user persona forward. In this instance, the primary goal is to improve productivity.
Imagine a user, Tech-Savvy Tim, immersed in his professional realm. His primary goal, a quest for heightened productivity, unveils a dedication to efficiency and excellence in his work.
Tim seeks tools and solutions that not only meet the demands of his tasks but elevate his overall work performance. Acknowledging this primary goal directs businesses toward developing features and functionalities that directly contribute to Tim's pursuit of enhanced productivity in his professional endeavors.
- Secondary goals
Explore the additional objectives that enrich your user's journey. In this case, the secondary goals involve staying updated on industry trends.
Consider Tim's broader aspirations beyond daily tasks. His secondary goals transcend the confines of immediate work, reflecting a desire to remain at the forefront of industry advancements.
Staying updated on industry trends signifies a proactive approach to professional growth and a commitment to staying relevant in a rapidly evolving landscape. Recognizing these secondary goals guides businesses in providing Tim with not just a product but a comprehensive solution that aligns with his continuous quest for knowledge and industry insights.
Step 5: Determine their pain points and challenges

Delving into the intricacies of your user's experiences unveils the hurdles and frustrations they encounter. Understanding their pain points and challenges is key to developing solutions that genuinely meet their needs.
- Pain points
Identify the specific pain points that cause discomfort or hinder your user's journey. In this instance, the pain point is a lack of efficient collaboration tools.
Picture our user, Tech-Savvy Tim, navigating through his daily tasks. The lack of efficient collaboration tools becomes a palpable frustration, hindering the seamless flow of work and impeding the collaborative spirit he values.
Recognizing this pain point offers businesses an opportunity to provide solutions that streamline collaboration, enhancing Tim's overall user experience and boosting his productivity.
- Challenges
Uncover the broader challenges that your user persona faces in their professional or personal landscape. In Tim’s case, keeping up with the latest technologies is a challenge.
Tim grapples with the ever-evolving tech landscape. Staying abreast of the latest technologies poses a continuous challenge, demanding a blend of adaptability and a constant thirst for knowledge.
Addressing this challenge goes beyond merely providing tools; it involves offering resources, insights, and features that align with Tim's aspiration to stay at the forefront of technological advancements. Acknowledging and catering to this challenge positions businesses as valuable allies in Tim's ongoing journey of professional growth.
Step 6: Understand user behavior
Analyzing the user behavior nuances unveils the patterns and motivations that shape their interactions with your product or service. This step is pivotal in tailoring your offerings to align seamlessly with their preferences and objectives.
- Behaviors
Delve into the specific actions and preferences exhibited by your user. In Tim’s case, the observed behaviors are a preference for mobile access and daily product usage.
Imagine our user, Tech-Savvy Tim, seamlessly integrating your product into his daily routine. His preference for mobile access signifies a dynamic and on-the-go lifestyle where flexibility is paramount. The daily utilization of the product showcases a consistent reliance on its features, emphasizing its integral role in Tim's workflow.
Recognizing such behaviors allows businesses to optimize the mobile experience and ensure that daily interactions remain intuitive and valuable to Tim.
- Motivations
Uncover the driving forces behind your user's engagement with your product or service. In this example, motivations include a quest for tools that streamline tasks and save time.
Consider Tim's motivations as he navigates the digital landscape in search of solutions. His primary drive lies in efficiency, a quest for tools that not only meet but exceed expectations in streamlining tasks and conserving valuable time.
Tim's motivations reflect a broader trend in users seeking products that align with their desire for productivity and a seamless user experience. Understanding and aligning with these motivations will allow you to enhance your product features, ensuring they resonate with Tim's overarching goal of optimizing his daily workflow.
Step 7: Create a user persona profile
Organize the gathered information into a structured format, physical or digital. Consider using user persona templates to do it quicker.
The result may look like this:
Step 8: Validate and refine
Share the persona with your team and gather feedback. Ensure that the persona accurately reflects your target audience. Make adjustments based on insights from stakeholders.
Step 9: Use personas in decision-making
Integrate personas into your design, marketing, or content strategy. When making decisions, consider how they align with your personas' needs and preferences.
Tip: Creating user personas is an ongoing process. Regularly update them based on new insights and changes in your target audience.
How to create a buyer persona?

Creating a buyer persona is crucial for businesses aiming to understand their target customers and tailor their marketing efforts accordingly. Here's how to do it, along with examples:
Step 1: Define your purpose and goals
Yet again, you need to clearly articulate why you need buyer personas. Are you creating them to inform marketing strategies, improve product development, or enhance customer experience?
Let’s review a few purpose-based cases:
- Inform marketing strategies
Purpose: By understanding your buyers on a more personal level, you can tailor your marketing strategies to speak directly to their needs and preferences. This leads to more targeted campaigns that are more likely to capture the attention and loyalty of your audience.
Example: If Marketing Maven Molly values brand visibility, a marketing or product strategy could be crafted around initiatives that specifically enhance your brand's visibility, such as influencer partnerships or visually appealing social media content.
- Improve product development
Purpose: An effective buyer persona provides valuable insights into what features, functionalities, or improvements your target audience is looking for. This information can guide product development teams in creating solutions that truly meet customer needs.
Example: If Molly faces budget constraints in her marketing initiatives, a product that offers cost-effective solutions or emphasizes a strong return on investment may be particularly appealing to her.
- Enhance your customers’ experience
Purpose: Understanding your buyers' goals, challenges, and preferred channels of interaction allows you to enhance the overall customer experience. From website design to customer support, aligning your efforts with the preferences of your personas fosters satisfaction and loyalty.
Example: If Molly prefers obtaining information through webinars and industry blogs, ensuring that your website offers easy access to such resources enhances her experience with your brand.
- Optimize sales strategies
Purpose: Good buyer personas empower sales teams with a deeper understanding of customers' motivations and pain points. This knowledge can be leveraged to refine sales pitches, overcome objections, and build stronger relationships with potential clients.
Example: Knowing Molly's focus on improving marketing ROI, a sales approach that highlights the cost-effectiveness and measurable returns of your product or service would likely catch her attention.
- Drive personalization across touchpoints
Purpose: Creating accurate buyer personas facilitates a personalized approach in communication across various touchpoints, including receiving emails, engaging with social media, and getting support. Personalization increases engagement and fosters a sense of connection with your brand.
Example: Sending personalized email campaigns to Molly that address her specific challenges and goals, rather than generic content, is more likely to capture her attention and drive action.
Clearly defining different purposes and goals at the outset ensures that creating buyer personas is a strategic endeavor, with tangible benefits rippling across marketing, product development, customer experience, and sales efforts. It sets the stage for a more informed and targeted approach to engaging with your audience.
Step 2: Conduct market research
Gathering comprehensive information about your target audience is a multifaceted process involving diverse sources. Here's an enriched explanation of each method:
- Develop surveys to collect relevant data, preferences, and buying behaviors
Launch surveys with clear objectives, ensuring questions delve into not only basic demographic information but also preferences and behaviors. This could include inquiries about preferred communication channels, product features, and factors influencing purchasing decisions.
Encourage survey participation by offering incentives, such as discounts or exclusive content. This not only boosts response rates but also demonstrates a commitment to value exchange with your audience.
Design surveys that allow for segmenting responses based on different criteria. This segmentation provides nuanced insights into diverse customer segments within your target audience.
- Use website analytics and sales data to understand customers' behavior
Dive deep into website analytics and sales data to uncover patterns and trends. This includes analyzing page views, bounce rates, conversion paths, and the performance of different products or services.
Integrate website analytics with your customer relationship management (CRM) system to connect online behavior with actual sales interactions. This holistic view provides a more complete understanding of the customer journey.

Look for points in the customer journey where users might drop off or encounter difficulties. Addressing these pain points can significantly improve the overall user experience.
- Conduct interviews with existing customers or potential buyers to gain qualitative insights
Interviews offer the opportunity for in-depth, open-ended conversations. Engage with both existing customers and potential buyers to understand their experiences, challenges, and aspirations.
Beyond factual information, delve into the emotions and motivations that drive customers' decisions. Uncover the "why" behind their actions, providing richer qualitative insights.
Establishing trust with interviewees is crucial. This trust encourages honest responses, fostering a more authentic representation of their perspectives.
- Analyze social media interactions and comments for customer sentiments
Leverage sentiment analysis tools to systematically analyze social media interactions and comments. These tools can categorize sentiments as positive, negative, or neutral, providing a quantitative measure of customers' sentiments.
Actively participate in social media conversations. Respond to comments, address concerns, and engage with your audience. This hands-on approach not only humanizes your brand but also provides real-time insights into customers' sentiments.
Monitor trends and assess whether the content is viral. Understanding what resonates with your audience on social media can inform content creation strategies and highlight areas for brand improvement.
By using a mix of methods, businesses can get a thorough and nuanced grasp of their target audience. This varied approach confirms findings from different sources and gives a complete picture that guides strategic decision-making in a well-rounded manner.
Step 3: Identify your buyer persona demographic information
Define the basic characteristics of your buyer persona. Just like with a user persona, those can be something like that:
- Age: 35 years old
- Gender: Female
- Occupation: Marketing Manager
- Location: Urban areas in the United States
Step 4: Explore goals and challenges
Take a deep dive into understanding what your buyers aspire to achieve and the hurdles they encounter along the way. This exploration helps to paint a vivid picture of their motivations and pain points.
- Goals
Uncover the ambitions that drive your buyers forward. In the example, the goals are to increase brand visibility and improve marketing return on investment (ROI).
Imagine Marketing Maven Molly striving to elevate her brand's visibility in a crowded market, aiming for a prominent presence that expects her target audience. Simultaneously, she seeks to optimize her marketing ROI, hoping to make every budgetary allocation count for impactful results. Understanding these goals provides a lens into Molly's overarching objectives and clarifies the outcomes she values most.
- Challenges
Identify the hurdles and limitations your buyers face. In Molly’s case, it's a limited budget for marketing initiatives.
Within Molly's professional landscape, the challenge may lie in navigating a marketing terrain with financial constraints. Acknowledging this constraint paints a more realistic portrait of her circumstances, prompting businesses to consider cost-effective solutions or innovative approaches that align with her budgetary restrictions. Recognizing and addressing these challenges forms the basis for tailoring solutions that correspond to Molly's specific circumstances.
Step 5: Determine buying behavior

Delve into the intricate journey your buyers embark on when making purchasing decisions. Understanding their decision-making process and preferred channels provides valuable insights into how to effectively engage with them.
- Decision-making process
Unearth the steps and considerations your buyers undertake as they navigate the path to a purchasing decision. In this example, the decision-making process involves researching online, seeking recommendations, and evaluating multiple options.
Imagine your buyer, Marketing Maven Molly, meticulously navigating the digital landscape. She starts with thorough online research, scouring the internet for information that aligns with her goals.
Seeking validation, Molly taps into her network, actively seeking recommendations from trusted sources. Finally, she adopts a discerning approach, carefully evaluating various options before arriving at a well-informed decision. This detailed understanding of Molly's decision-making process allows businesses to align their strategies with each stage, providing the relevant information and support she seeks at every turn.
Preferred channels
Identify the platforms and avenues where your buyers are most receptive to communication. In this instance, preferred customer channels include social media, industry forums, and email newsletters.
Visualize Molly seamlessly navigating her preferred channels. She immerses herself in the dynamic conversations of industry forums, absorbing insights and engaging with peers. Social media becomes a canvas for her exploration, offering bite-sized content and interactions that interest her on a personal level.
At the same time, Molly values the curated content delivered through email newsletters, appreciating the tailored information that aligns with her professional interests. Recognizing and respecting these preferred channels allows businesses to tailor their outreach, ensuring a more impactful and personalized connection with Molly throughout her buying journey.
Step 6: Find out information sources
Pinpointing the avenues where buyers seek information is crucial for tailoring your outreach. Understanding their preferred information sources and trusted platforms sheds light on where your target audience is most receptive.
- Information sources
Uncover the diverse channels and resources where buyers turn for information. In this example, information sources include industry blogs, webinars, and social media influencers.
Envision Marketing Maven Molly on her quest for knowledge. She immerses herself in the in-depth insights of industry blogs, craving the expertise and nuanced perspectives they offer. To stay on the cutting edge, Molly actively participates in webinars, leveraging these interactive sessions for deep dives into emerging trends.
Additionally, she values the authentic voice of social media influencers, appreciating the distilled wisdom and real-world experiences they bring. Recognizing these preferred information sources allows businesses to curate content that aligns with Molly's expectations, establishing credibility and trust in the process.
- Trusted platforms
Identify the platforms where your buyers place their trust for gathering information. In Molly’s case, trusted platforms include LinkedIn for professional insights and Instagram for visual content.
Imagine Molly navigating the digital landscape with discernment. LinkedIn emerges as her go-to platform for professional insights, where she engages with thought leaders, industry updates, and meaningful discussions.
Instagram is her visual haven, a space where compelling visual content captures her attention and provides a different dimension to her information consumption. Recognizing these trusted platforms enables businesses to strategically position their content, ensuring it seamlessly aligns with the platforms Molly trusts for reliable and valuable insights.
Step 7: Create a buyer persona profile
Organize the gathered information into a structured format.
Step 8: Validate and refine
Share the buyer persona with your team and stakeholders, and gather feedback. Ensure that the persona accurately reflects your target audience. Make adjustments based on insights from those involved in sales, marketing, and product development.
Step 9: Use buyer personas
Integrate buyer personas into your marketing and sales strategies. Tailor your messaging, content, sales, and advertising efforts to align with the needs and preferences of your buyer personas.
Summary
Knowing the difference between buyer and user personas is crucial for many reasons. Identifying goals, expectations, motivations, and pain points can provide valuable insights into which features to focus on.
Key takeaways:
- Buyer personas aren't necessarily users, but they can be.
- User personas focus on details such as ease of use, while buyer personas are more about higher-level goals.
- Keep in mind that a buyer persona may be a team of decision-makers with different goals and expectations.
- Finding out how much influence user personas have on the final decision can be beneficial.
- Do not forget to focus on skills and previous experience when creating user personas.
Managing hoards of personas can be very frustrating, so you might want to check out the UXPressia persona creation tool, an online solution for creating, storing, managing, sharing, and exporting user and buyer personas. It is easy to use, and it has a forever free plan. Better yet, start with our free B2B Persona template you see above:






So if the buyer persona and the user are not the same, like when you’re getting a computer for your mom. Does that mean their customer journeys won’t have anything in common since where one ends, the other begins?
Great question, Ollie! You guessed right that these journeys likely won’t be end-to-end ones. For example, the user (mom) won’t be going through awareness, research, and purchase stages. She joins in later on for the delivery and use. However, if she isn’t too tech-savvy, she might have trouble with filing a support claim. And her son, the buyer, will take over for the complaint stage.
Their experiences and goals are different. But their stages can overlap, and so can the sections you use to describe their experience. To keep up with these nuances, you can actually visualize both of their journeys on the same map. We have more information on how to do that in this post: https://uxpressia.com/blog/multiple-persona-journeys
Really helpful breakdown of user vs. buyer personas! This is essential for tailored marketing strategies.